44 dosage calculations from medication labels
› health › dosageDosage Calculator - How to Calculate Dosage? Dosage calculation formulas. If you want to calculate the dose of a medication, you need to use the following equation: dose = weight * dosage. where: weight — Patient's weight, expressed in kg or lb. It is very important that you input an accurate result; dosage — Prescribed amount of drug in mg per kg of body weight. Oral Drug Dosage Calculator - Liquid Solution Syrup This calculator determines the volume of liquid, solution or syrup to be administered to the patient. The label on the medicine bottle states the concentration of the medicine. The concentration is the mass of medicine contained in a volume of liquid. The mass is the have dose. The volume is the quantity. Notes:
Nursing Pharmacology: Dosage and Calculations Practice Test Dosage and Calculations Practice Tests are some of the most commonly-searched practice exams for both student nurses and nurses wanting to take licensure and certification exams. ... The medication label reads "when reconstituted with 7.4 mL of bacteriostatic water, the final concentration is 1 g/7.4 mL." ...

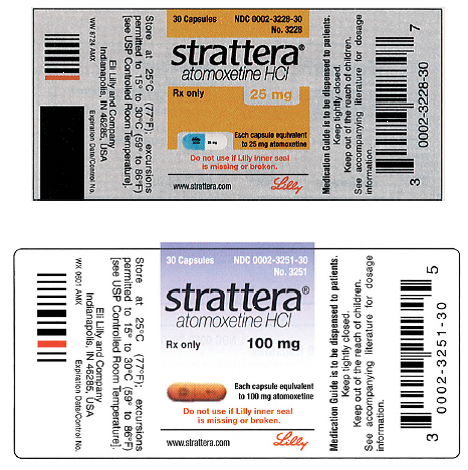
Dosage calculations from medication labels
PDF Introductory Level Drug Dosage Practice Problems dosage for this patient using the medication label below. Give: _____ mL 22. A patient has a severe migraine, and the doctor prescribes 18 mg of S umatriptan subcut stat. Use the label below to calculate the correct dosage fo r the patient. Give: _____ mL 23. A patient develops a post-operative vitamin B12 deficiency, so the doctor prescribes 2 › math104 › lecture3Lecture 3: Reading Medication Labels and Basic Dosage ... Tuberculin syringe: A tuberculin syringe is used to measure small doses, so it is often used to dose small children and infants.There are two different sizes of tuberculin syringes which you might encounter: one kind can hold a total of 1 mL, and another kind can hold a total of 0.5 mL; every hundredth of a mL is marked on a tuberculin syringe, and every fifth of a mL is labeled; this means ... PDF Preparing for the Drug Dosage Calculation Competency Exam BSN ... Dosage by weight (with label) 2 Continuous IV med (flow rate or medication delivered) 2 Direct IV (IV push) (with label if possible) 2 Total 20 Recommended text: Olsen, J., Giangrasso, A. & Shrimpton, D. (2015). Medical dosage calculations: A dimensional analysis approach. Boston, MA: Pearson
Dosage calculations from medication labels. Reading Medication Labels | Basicmedical Key CHAPTER 13 Reading Medication Labels Objectives After reviewing this chapter, you should be able to identify: 1. The trade and generic names of medications 2. The dosage strength of medications 3. The form in which a medication is supplied 4. The total volume of a medication container where indicated 5. Directions for mixing or preparing a drug where necessary 6. PDF Drug Dosage & IV Rates Calculations - George Brown College Dosage calculations based on body weight are required when the dosage ordered and administered is dependent on the weight of the patient. For example, many pediatric ... dosage range listed on the medication label. 750 mg is within the desired range of 699-1398 mg since 699 < 750 < 1398 Therefore, the doctor has ordered a dosage within the ... PDF Dosage Calculations Syllabus(1)new - Odessa College Chapter 6: Oral medication labels and dosage calculations (CO #1-5) The learner will: 1. Identify scored tablets, unscored tablets, and capsules. 2. Read drug labels to identify trade and generic names. 3. Locate dosage strengths and calculate average dosages. 4. Measure oral solutions using a medicine cup. Chapter 7: Safe medication administration PDF Basic Medication Calculations 10. Medication: 400mg of Dopamine Volume of Fluid: 250 ml Order is in: mcg 11. Medication: 2g of Lidocaine Volume of Fluid: 1000ml Order is in: mg 12. Medication: 5g of Bretylium Volume of Fluid: 500ml Order is in: mg 13. Medication: 1600mcg Dopamine Volume of Fluid: 1000ml Order is in: mcg 14. Medication: 2mg of Lidocaine Volume of Fluid: 250ml
Calculating from the labels | Learning Lab Calculating from the labels. This short video is the second of three videos in the Nursing calculations - Finding the volume required section. It explains how to calculate medication dosage from labels using the method of mental calculation and proportinality to get the right dosage for drugs in solution. YouTube. RMIT University Library Videos. › nclex › dosage-calculationsDosage Calculations: NCLEX-RN || RegisteredNursing.org Here is an example of how to calculate oral medication dosage using ratio and proportion: Doctor's order: 125 mg of medication once a day. Medication label: 1 tablet = 250 mg ... Medication label: Meperidine 40 mg/mL. How many mL or cc will you give for each prn dose? Using ratio and proportion, this problem is set up and solved as shown below. ... Drug Calculations Practice NCLEX Questions (100+ Items) - Nurseslabs In this section are the practice problems and questions for nursing dosage calculations. This nursing test bank set includes 100+ questions broken down into four parts. Included topics are dosage calculation, metric conversions, unit conversions, parenteral medications, and fluid input and output. As you can tell, this NCLEX practice exam ... Tablet Dosage Calculation - Basic-mathematics.com A few examples showing how to do tablet dosage calculation. Example #1: Say the dosage strength is 100 mg and there are 200 tablets in the bottle. If the doctor orders 300 mg, how many tablets will you give? 100 mg + 100 mg + 100 mg = 300 mg. As you can see, you need 3 tablets of 100 mg to reach the dosage of 300 mg ordered by the doctor.
Dosage Calculation Resources - Calhoun Community College Calculation problems will be fill-in-the-blank, NOT multiple choice. If you need testing accommodations contact Student Disability Services at 256-306-2630; Study Guides. Session 1 Basic Review; Session 2 Systems of Measurement.pptx; Session 3 Methods of Administration 2; Session 4 Medication Labels; Session 5 Formula Method and Ratio to ... How to Read a Medication Label Nursing Quiz A. 7 doses. B. 5 doses. C. 20 doses. D. 12 doses. The answer is C (20 doses). The total volume amount after reconstitution (meaning once the nurse has mixed the medication) is 100 mL. The label tells us that in 5 mL of this medication there are 350 mg. The patient needs to take 350 mg twice a day. Nursing Math - Parenteral Injectable Drug Dosage Calculator Parenteral Drug Dosage Calculator For Syringe Liquid Solutions Medicine Injectable Dosage Equations Formulas. Description: This calculator determines the liquid or solution volume to be injected by syringe into the patient. The label on the medicine bottle states the concentration of the medicine. The concentration is the mass of medicine ... Clinical Calculations: Module 6: Divided Doses and Reconstituted ... Problems will involve reading medication labels and healthcare provider's orders. You will calculate the correct amount to give a client of oral, injectable, and intravenous medications. Assume all questions ask for the amount per dose unless instructed otherwise. Equivalents to know. You should now know all your commonly used equivalents.

Dosage Calc - The nurse's quick guide to I.V drug calculations Basic dosage calculations D ...
webcontent.indianhills.edu › lu03_calculationsFormulas for Calculating Medication Dosage the medication label, and Q (quantity) is the volume in which the dosage strength is available (e.g. tablets, capsules, milliliters). For example: we have an order for Ceclor 0.5 g PO b.i.d. We have available 250 mg capsules. The first thing to do is get like units of measurement. Since we have 250 mg capsules, let's change our ordered dose ...
› drug-dosage-calculationsDrug Dosage Calculations | How-to-guide + Quiz | KnowledgeDose Sep 20, 2019 · Drug Dosage Calculation Formulas. To calculate the number of tablets, use the following formula: Strength required / Stock strength = Number of tablet(s) required. Or another way this drug dosage formula can be expressed is: What you want / What you’ve got = Number of tablet(s) required. To calculate the volume dose for liquid medicine, use this formula: (Strength required / Stock strength) × Stock volume = Volume dose required

Pediatric Safe Dosage Calculations Quiz | Nursing | Pinterest | Dosage calculations, Nurse stuff ...
Dose Calculation Dimensional Analysis Factor-Label Method Three primary methods for calculation of medication dosages exist, and these include dimensional analysis, ratio proportion, and formula or desired-over-have method. ... The dimensional analysis approach or the factor-label method can be used to provide an additional safety check with the other methods of calculation. The correct dose should be ...
› books › NBK493162Dose Calculation Desired Over Have Formula Method ... There are 3 primary methods for the calculation of medication dosages, as referenced above. These include Desired Over Have Method or Formula, Dimensional Analysis, and Ratio and Proportion (as cited in Boyer, 2002)[Lindow, 2004]. ... Dose Calculation Dimensional Analysis Factor-Label Method. Toney-Butler TJ, Wilcox L. StatPearls. 2022 Jan ...
Drug Calculations Involving Reading Drug Labels, Part 1 - YouTube Practice performing drug dosage problems that require the use and understanding of drug labels to solve. Problem 1.) Determine the milliliters of Augmentin ...
Dosage Calculation Using the Formula Method - Basicmedical Key 2. Calculate medication dosages using the formula. D H × Q = x. 3. Calculate the number of tablets or capsules to administer. 4. Calculate the volume to administer for medications in solution. This chapter shows how to use a formula for dosage calculation, which requires substituting information from the problem into the formula. The nurse ...
ATI Dosage Calculations 3.0: Oral Medications Flashcards & Practice ... Start studying ATI Dosage Calculations 3.0: Oral Medications. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Home. Subjects. Explanations. Create. Study sets, textbooks, questions. ... Refer to the medication label below. How many mL should the nurse administer?
Drug Calculations: How To Use Dimensional Analysis Step 2: On the right side, place the information given with the same label needed in the numerator. In this example, we know that the drug concentration available is 0.25 mg/mL. Place mL in the numerator and 0.25 mg in the denominator. Step 3: The desired dose is 0.5 mg. Place information with the same label as the preceding denominator into ...

(PDF) Extracting Daily Dosage from Medication Instructions in EHRs: An Automated Approach and ...
PDF Medication Calculation Examination Study Guide Label shows 75 - 150 mg/kg per day. Is the physician's order within normal range? Solution: 6 x 75 = 450 mg (minimum dosage per day); 150 X6 = 900 (maximum dosage per day) 24 ÷ 4 = 6 dosages : 300 x 6 = 1800. Answer: Dosage is not within range. IV Calculations • [amount of fluid to be infused] x [drop factor] ÷ minutes to infuse = gtts/min
Dosage and Calculations - Registered Nurse RN How to read a medication label quiz for nursing students! It is very important a nurse knows how to read a medication label. Many times the drug label details the brand and generic name, dosage strength, volume amount, expiration date, route of administration, and contains important medication instructions. One of the reasons a nurse needs […]
Dosage Calculations Made Easy | Reconstitution Calculation Medication ... Dosage Calculations Nursing Students: This video demonstrates how to solve dosage and calculation problems for reconstitution of medications. I use dimension...
PDF Preparing for the Drug Dosage Calculation Competency Exam BSN ... Dosage by weight (with label) 2 Continuous IV med (flow rate or medication delivered) 2 Direct IV (IV push) (with label if possible) 2 Total 20 Recommended text: Olsen, J., Giangrasso, A. & Shrimpton, D. (2015). Medical dosage calculations: A dimensional analysis approach. Boston, MA: Pearson
› math104 › lecture3Lecture 3: Reading Medication Labels and Basic Dosage ... Tuberculin syringe: A tuberculin syringe is used to measure small doses, so it is often used to dose small children and infants.There are two different sizes of tuberculin syringes which you might encounter: one kind can hold a total of 1 mL, and another kind can hold a total of 0.5 mL; every hundredth of a mL is marked on a tuberculin syringe, and every fifth of a mL is labeled; this means ...
PDF Introductory Level Drug Dosage Practice Problems dosage for this patient using the medication label below. Give: _____ mL 22. A patient has a severe migraine, and the doctor prescribes 18 mg of S umatriptan subcut stat. Use the label below to calculate the correct dosage fo r the patient. Give: _____ mL 23. A patient develops a post-operative vitamin B12 deficiency, so the doctor prescribes 2











Post a Comment for "44 dosage calculations from medication labels"